Pes Anserine Bursitis
What Is Pes Anserine Bursitis?
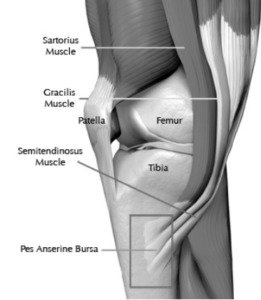 The Sartorius, Gracilis, and Semitendinosus are three muscles act to bend the knee, bring the knees together, and cross the knees. The Tendons of these three muscles (pes anserine) attach to the shin bone (tibia) over a bursa at the inside of the knee.
The Sartorius, Gracilis, and Semitendinosus are three muscles act to bend the knee, bring the knees together, and cross the knees. The Tendons of these three muscles (pes anserine) attach to the shin bone (tibia) over a bursa at the inside of the knee.
A bursa is a fluid filled sac that acts as a cushion between tendons, bones, and skin. Pes anserine bursitis is an irritation or inflammation of this bursa located on the inner side of the knee just below the knee joint.
What Are The Causes Of Pes Anserine Bursitis?
Bursitis, an inflammation of a bursa, usually develops as the result of overuse or chronic irritation. Pes anserine bursitis is common in swimmers who do the breaststroke and is sometimes called breaststroker’s knee. Pes anserine bursitis is common in athletes, particularly runners and with sudden distance changes. Kicking a ball repeatedly will also cause bursitis.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Bursitis?
- Pain and tenderness on the inside of your knee, approximately 2 to 3 inches below the joint, are symptoms of pes anserine bursitis of the knee.
- Pain increasing with exercise or climbing stairs
- Symptoms of pes anserine bursitis may mimic those of a stress fracture
What Are The Risk Factors Of Pes Anserine Bursitis?
As bursitis is commonly caused through over exerstion there are a few factors that lead to that including the lack of stretching before activities. There is also an increase of bursitis seen with patient who have osteoarthritis, obesity, and tight hamstrings.
How Is Bursitis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pes anserine bursitis begins with a history and physical examination. The exam will test the tenderness over the pes bursa X-rays will most likely be ordered to make sure that there are no other abnormalities in the knee. MRI can show inflammation of the bursa and other causes of knee pain.
What Are The Possible Treatments For Bursitis?
Treatment begins non-surgically and may include the following:
- Rest
- Ice (Cold Therapy) on your inner knee 3-4 times every day for 20 minutes
- Anti-inflammatory Treatments
- Physical Therapy for stretching & strengthening of the hamstrings, adductors, quadriceps
- Corticosteroid injection into the bursa to reduce the pain and swelling
Contact Robotic Joint Center today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Buechel.
